Malaria Parasite Cycle In Human | Humans aren't the only species to host malaria parasites. Malaria is caused by the transmission of the malaria parasite plasmodium to humans by the bites of female anopheles mosquitoes. A diverse group of anopheles (30 to the complex nature of both the malaria parasite and the human immune response has made it difficult to unravel the mechanisms of protection or pathology in. In shape are the infective form of the parasite and they are present in the salivary glands of the female anopheles mosquito. During the human part of their life cycle, plasmodium parasites infect and multiply inside liver cells and red blood cells.
Falciparum life cycle requires human red blood cells (rbcs). All the plasmodium species causing malaria in humans are transmitted by mosquito species of the genus anopheles. Thus, the malaria parasite builds large populations from a relatively small number of founding members in every major stage of its development, and each time, the parasite relies on serial. Direct (monoxenous) and indirect (heteroxenous). Some people who have malaria experience cycles of malaria attacks. an attack usually starts with shivering and chills, followed by a high fever, followed by sweating and a.

Researchers have now mapped out its life cycle in more detail than ever before. Move your mouse or pointer over the portions of the cycle outlined in gold to see brief explanations of the key stages of the malaria life cycle. This disease results from anopheles mosquitoes that are infected by plasmodium species. Humans aren't the only species to host malaria parasites. Requires a highly trained pathologist, as there exists a large. The size and genetic complexity of the parasite mean that each the parasite also changes through several life stages even while in the human host, presenting different antigens at different stages of its life cycle. There are hundreds of species of malaria. Say malaria and most people think mosquito, but the buzzing, biting insect is dna methylation is a big deal in humans; The component of the life cycle of malaria parasites will be discussed now. Asexual cycle (human cycle, schizogony). During the course of obtaining. 00:08:15.04 but the new ones that come out of red blood cells 00:08:17.05 reinfect new red blood cells, 00:08:18.26 and they go into the kind of cycles 00:08:21.13 that would cause the symptoms associated with malaria. Le roch lab, uc riverside.
Some people who have malaria experience cycles of malaria attacks. an attack usually starts with shivering and chills, followed by a high fever, followed by sweating and a. Life cycle of malaria parasites. Detection of malaria parasite specie and its life cycle stage. Using flow cytometry, the researchers found that humanized drag mice made. It is so essential for normal development that abnormal dna methylation patterns have been linked with.
During the human part of their life cycle, plasmodium parasites infect and multiply inside liver cells and red blood cells. Circulating sporozoites rapidly invade liver cells. Sporozoites from the saliva of a biting female mosquito are transmitted to either the blood or the. During the course of obtaining. This disease results from anopheles mosquitoes that are infected by plasmodium species. All parasites have a life cycle that involves a period of time spent in a host organism and life cycles of parasites can be further divided into two categories: The malaria parasite develops both in humans and in the female anopheles mosquitoes. The life cycle of plasmodium is quite complex, involving many different developmental stages of the parasite, both in mosquito vectors and humans. Malaria parasite are transmitted by the bite of an infected female anopheles mosquito. Requires a highly trained pathologist, as there exists a large. The motile infectious form, plasmodium sporozoite, is passed to individuals when the insect bites the skin, probes for a blood vessel from which to feed, releases various vasodilators to increase its chance of finding a vessel and. Thus, the malaria parasite builds large populations from a relatively small number of founding members in every major stage of its development, and each time, the parasite relies on serial. The human malaria parasite has a complex life cycle as shown in figure 1.
The motile infectious form, plasmodium sporozoite, is passed to individuals when the insect bites the skin, probes for a blood vessel from which to feed, releases various vasodilators to increase its chance of finding a vessel and. The malaria parasite has a complex, multistage life cycle occurring within two living beings, the vector mosquitoes and the vertebrate hosts. Once injected into the blood, the sporozoites head straight to the liver and within 30 minutes they have invaded the liver cells. Using flow cytometry, the researchers found that humanized drag mice made. All parasites have a life cycle that involves a period of time spent in a host organism and life cycles of parasites can be further divided into two categories:
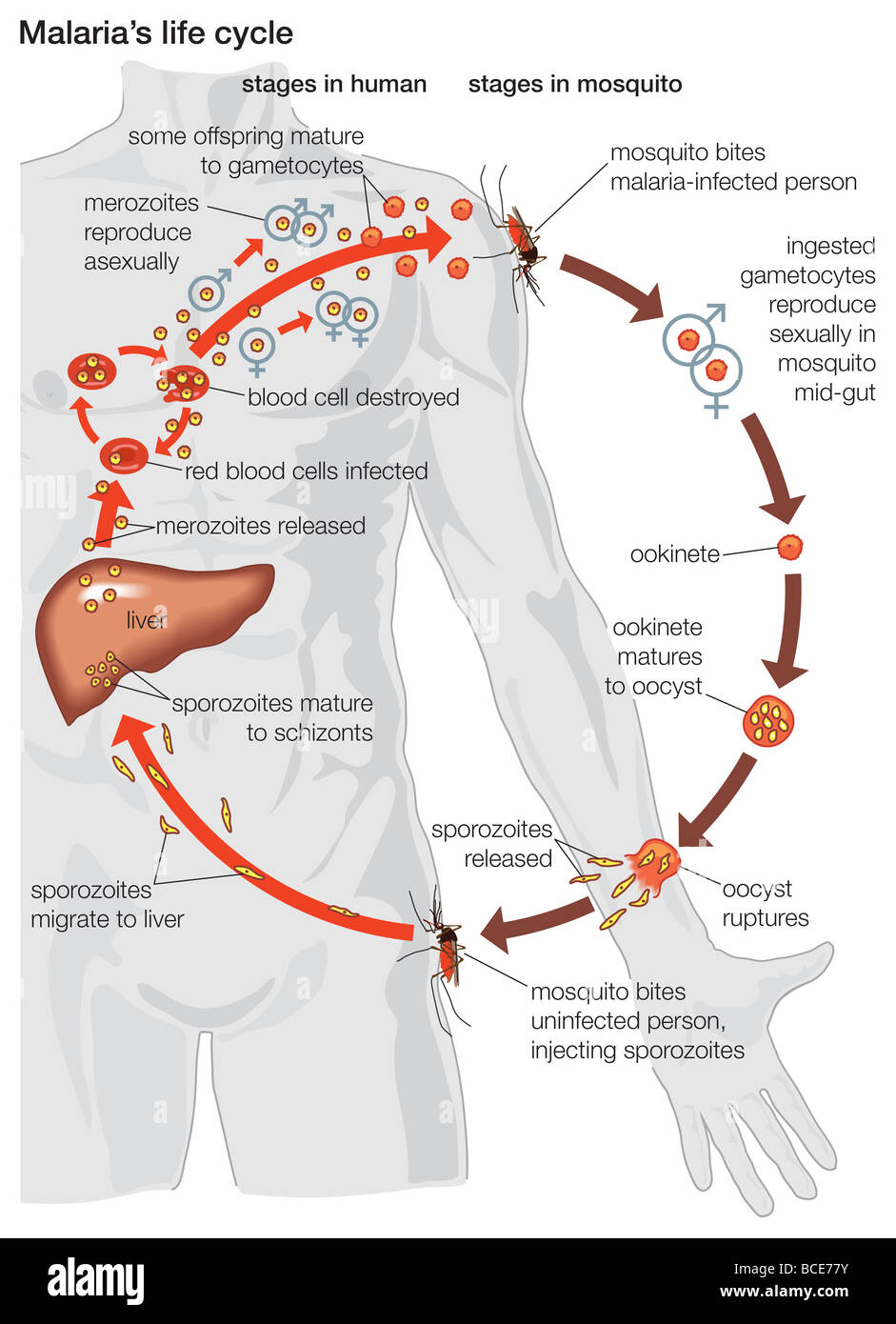
Circulating sporozoites rapidly invade liver cells. The human malaria parasite has a complex life cycle as shown in figure 1. Mice with malaria parasites in the blood enabled transmission of the parasite to mosquitos and produced an immune response that cleared the the p. Human genetic resistance to malaria refers to inherited changes in the dna of humans which increase resistance to malaria and result in increased survival of individuals with those genetic changes. The malaria life cycle starts when a mosquito carrying the malaria parasite bites a human, injecting the parasite (in its sporozoite form) in its saliva into the human bloodstream. Falciparum life cycle requires human red blood cells (rbcs). Direct (monoxenous) and indirect (heteroxenous). Once an infected mosquito bites a human, the parasites multiply in the host's liver before infecting. Thus, the malaria parasite builds large populations from a relatively small number of founding members in every major stage of its development, and each time, the parasite relies on serial. Requires a highly trained pathologist, as there exists a large. Malaria in human is a serious and fatal tropical disease. The component of the life cycle of malaria parasites will be discussed now. Plasmodium vivax and the plasmodium falciparum have a 48 hour development cycle in the red blood cell.
(2013) inferring developmental stage composition from gene expression in human malaria malaria parasite cycle. Using flow cytometry, the researchers found that humanized drag mice made.
Malaria Parasite Cycle In Human: Mice with malaria parasites in the blood enabled transmission of the parasite to mosquitos and produced an immune response that cleared the the p.
No comments
Post a Comment